使用Leaflet创建地图拓扑图
目录
目录[-]
之前我们采用过 Openlayers+Qunee的方案,实现地图拓扑图,鉴于Openlayers是一个古老项目,略显臃肿,对于现代的前端地图应用,显得笨重,在客户的介绍下,我们找到了leaflet – 基于HTML5的轻量地图客户端方案,结合Qunee使用,以及第三方插件,实现更加轻快的地图拓扑图应用 Leaflet介绍 leaflet是一个开源软件,作者在乌克兰,在移动设备上的有良好的体验,比较新和现代的地图客户端,类库压缩后只有33k,非常小巧,这一点让qunee都相形见绌,先看一个leaflet的入门示例
官方示例
首先引入leaflet相关js和css
<link rel="stylesheet" href="http://cdn.leafletjs.com/leaflet-0.7.3/leaflet.css" />
<script src="http://cdn.leafletjs.com/leaflet-0.7.3/leaflet.js"></script>
然后构建地图,并添加openStreetMap
// create a map in the "map" div, set the view to a given place and zoom
var map = L.map('map').setView([51.505, -0.09], 13);
// add an OpenStreetMap tile layer
L.tileLayer('http://{s}.tile.osm.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png').addTo(map);
// add a marker in the given location, attach some popup content to it and open the popup
L.marker([51.5, -0.09]).addTo(map)
.bindPopup('A pretty CSS3 popup.
Easily customizable.')
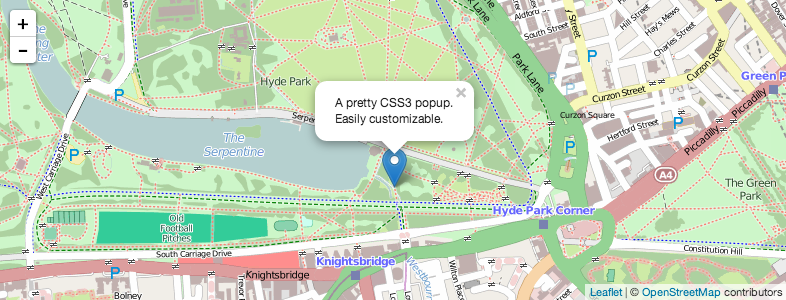
.openPopup();运行效果如下:
结合Qunee拓扑图
Leaflet地图上可以添加点线面基本图形,如果需要展示更复杂的图形或者链接关系,显得力不足,可以结合Qunee组件使用,下面我们让地图和拓扑图叠加起来,在地图上显示拓扑元素,并整合两者的交互
图层叠加
在地图的DIV容器中添加一个孩子div,作为拓扑图的画布,并设置相应的css,然后调用超类的构造函数,取消默认的双击和滚轮操作,已被后面地图与拓扑图的交互同步
var MapGraph = function (map) {
var container = map._container;
var canvas = document.createElement("div");
canvas.style.width = "100%";
canvas.style.height = "100%";
container.appendChild(canvas);
Q.doSuperConstructor(this, MapGraph, [canvas]);
this.enableWheelZoom = false;
this.enableDoubleClickToOverview = false;
this.originAtCenter = false;
this.setMap(map);
...
}
关联地图
下面实现拓扑图与地图的绑定,在#setMap(map)函数中,监听了地图的zoomstart和zoomend事件,根据经纬度动态的调整图元的屏幕位置,同样在节点被拖动后,也需要设置新的经纬度
MapGraph.prototype = {
map: null,
mapShowing: true,
enableInertia: false,
createNodeByLonLat: function (name, lon, lat) {
var l = this.toLonLat(lon, lat);
var p = this.getPixelFromLonLat(l);
var node = graph.createNode(name, p.x, p.y);
node.lonLat = l;
return node;
},
toLonLat: function (lon, lat) {
return new L.latLng(lat, lon);
},
getPixelFromLonLat: function (lonLat) {
return this.map.latLngToContainerPoint(lonLat, this.map._zoom);
},
getLonLatFromPixel: function (x, y) {
return this.map.containerPointToLatLng([x, y]);
},
setMap: function (map) {
this.map = map;
this.map.on("zoomstart", this.hideGraph, this);
this.map.on("zoomend", this.updateNodes, this);
this.html.ondblclick = createEventFunction(this, function (evt) {
if (this.getElementByMouseEvent(evt)) {
Q.stopEvent(evt);
}
});
this.interactionDispatcher.addListener(function (evt) {
if (evt.kind == Q.InteractionEvent.ELEMENT_MOVE_END) {
var datas = evt.datas;
Q.forEach(datas, function (data) {
var pixel = this.toCanvas(data.location.x, data.location.y);
data.lonLat = this.getLonLatFromPixel(pixel.x, pixel.y);
}, this);
}
}, this)
},
hideGraph: function(){
this.html.style.visibility = "hidden";
},
showGraph: function(){
this.html.style.visibility = "";
},
translate: function (tx, ty) {
Q.doSuper(this, MapGraph, "translate", arguments);
this.map.panBy([-tx, -ty], {animate: false});
},
resetVisibility: function () {
this.forEach(function (e) {
if (e.invalidateVisibility) {
e.invalidateVisibility(true);
}
});
},
updateNodes: function () {
this.translateTo(0, 0, 1, true);
this.resetVisibility();
this.forEach(function (d) {
if (d instanceof Q.Node) {
var l = d.lonLat;
var p = this.getPixelFromLonLat(l);
d.location = p;
}
}, this);
this.showGraph();
}
}
Q.extend(MapGraph, Q.Graph);此外还可以通过可见过滤器实现,不同比例尺显示不同的节点
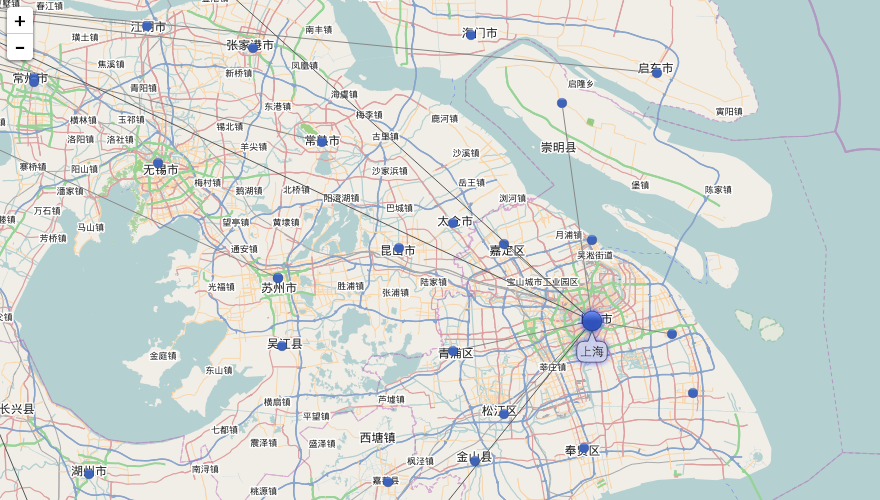
运行效果
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/jsrookie/article/details/84804405