ArcEngine 数据查询、数据操作总结
目录
数据查询
查询地理数据库表
查询geodatabase对象的三种常见的接口是IQueryFilter、ISpatialFilter、IQueryDef接口。每个接口都有不同的功能,如下表所示:
| Requirement | IQueryFilter | ISpatialFilter | IQueryDef |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apply attribute constraints(支持属性约束) | True | True | True |
| Apply spatial constraints (支持空间约束) | False | True | False |
| Query results contain fields from multiple tables (查询结果包含多个表的字段,可理解为支持多表连接查询) | False | False | True |
| Query results returned as a cursor (查询结果返回一个游标对象) | True | True | True |
| RecordSet objects can be created from results (从结果可以创建记录集对象) | True | True | True |
| Returned records can be edited (查询结果可以被编辑) | True | True | False |
| Records include edits made in active edit session | True | True | False |
IQueryFilter接口
属性及方法详解
- SubFields
使用技巧:查询的时候只需设置需要的字段即可,比如你要查询age>15的数据,设置成SubFields=“age”就好了,这样在查询上效率会有所提高,如果不设置该属性,默认查询所有字段(相当于是“*”);如果需要返回全部字段采用默认值即可,不要把SubFields设置为”*”和”“。 - WhereClause
使用技巧:查询条件的语法取决于你使用的数据源,应用程序可以使用ISQLSyntax接口在一个工作空间来确定使用的SQL语法信息,如用于限定表和字段名称和标识引用字符的划界字符。
参考链接:传送门
相关参考资料:待上传……
注意事项:不支持Distinct关键字
相关接口
- IQueryFilterDefinition (可用此接口进行Group By和Order By操作)
- ISQLSyntax
示例代码
// 创建过滤器对象
IQueryFilter queryFilter = new QueryFilterClass();
// 设置查询字段
queryFilter.SubFields = "NAME, ADDRESS";
// 设置查询条件
queryFilter.WhereClause = "TYPE = 'Restaurant'";
// 接口跳转到IQueryFilterDefinition接口,利用它的PostfixClause属性来对某个字段排序
IQueryFilterDefinition queryFilterDef = (IQueryFilterDefinition)queryFilter;
queryFilterDef.PostfixClause = "ORDER BY NAME";
// 读取查询结果
int nameIndex = table.FindField("NAME");
int addressIndex = table.FindField("ADDRESS");
//用ComReleasr对象管理Com对象的生命周期,保证Com对象的释放
Using(ComReleaser comReleaser = new ComReleaser())
{
ICursor cursor = table.Search(queryFilter, true);
comReleaser.ManageLifetime(cursor);
IRow row = null;
while ((row = cursor.NextRow()) != null)
{
String name = Convert.ToString(row.get_Value(nameIndex));
String address = Convert.ToString(row.get_Value(addressIndex));
Console.WriteLine("{0} - {1}", name, address);
//这块强烈建议row释放掉,如果做大数据操作的时候这块不释放 内存会撑爆的。
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(row);
}
}使用小窍门
- 查询游标True和False的区别
- True
循环使用对象,查询速度快,只存储一份对象 - False
不循环使用对象,查询速度慢,存储多份对象
- True
- Fields设置技巧
只设置需要查询的字段,这样比不设置和设置*查询速度会快很多 - WhereClause使用技巧
优先使用大于、小于,其次才是不等于
ISpatialFilter接口
属性及方法详解
- Geometry
查询要素的的空间过滤条件(几何对象),设置的Geometry对象必须实现IRelationalOperator接口,如高级别的几何对象(points, polylines, polygons, and geometry bags),该属性不支持低级别的几何对象(lines, paths and rings)。 - GeometryField
查询要素类的几何字段
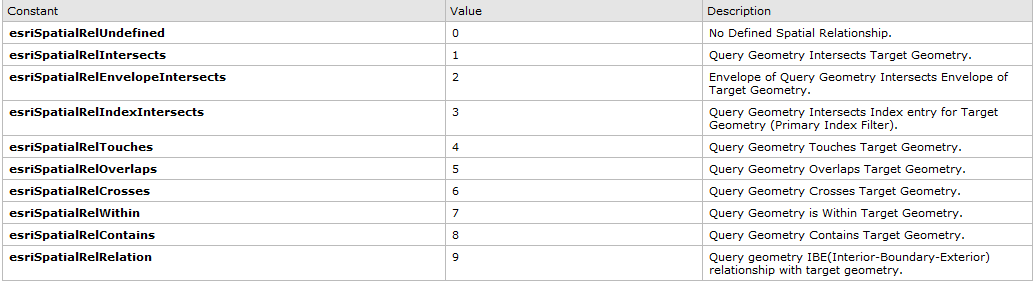
-SpatialRel
要素类和查询图形的几何关系,具体设置参考官方文档
- 其它参数
请参考帮助文档
相关接口
相关接口同IQueryFilter
示例代码
// 创建一个查询范围
IEnvelope envelope = new EnvelopeClass();
envelope.PutCoords( - 84.4078, 33.7787, - 84.3856, 33.7997);
// 创建一个空间过滤器,并设置其相关的属性
ISpatialFilter spatialFilter = new SpatialFilterClass
{
Geometry = envelope, //空间过滤条件
GeometryField = featureClass.ShapeFieldName, //空间字段名称
SpatialRel = esriSpatialRelEnum.esriSpatialRelIntersects //空间关系
};
// Set the attribute constraints and subfields.
// 设置属性过滤条件
spatialFilter.WhereClause = "NAME <> 'Ramp' AND PRE_TYPE NOT IN ('Hwy', 'I')";
// 设置属性查询的字段
spatialFilter.SubFields = "NAME, TYPE";
// 获取查询字段的索引
int nameIndex = featureClass.FindField("NAME");
int typeIndex = featureClass.FindField("TYPE");
//使用ComReleser管理Com对象
using(ComReleaser comReleaser = new ComReleaser())
{
//读取查询结果
IFeatureCursor featureCursor = featureClass.Search(spatialFilter, true);
comReleaser.ManageLifetime(featureCursor);
IFeature feature = null;
while ((feature = featureCursor.NextFeature()) != null)
{
String roadName = Convert.ToString(feature.get_Value(nameIndex));
String roadType = Convert.ToString(feature.get_Value(typeIndex));
Console.WriteLine("Name: {0}, Type: {1}", roadName, roadType);
//这块强烈建议feature释放掉,如果做大数据操作的时候这块不释放 内存会撑爆的。
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(feature);
}
}使用小窍门
If a geometry bag is being used as the filter’s query geometry, create a spatial index for the geometry bag before being assigned to the geometry property. This can drastically increase the query’s efficiency. The following code example shows how to do this:
如果使用几何包对象作为过滤的几何图形,在为ISpatialFilter对象设置Geometry属性之前,先对几何包对象创建空间索引,这样能大大提高查询的效率,下面是创建空间索引的示例代码:
// 将几何包对象转换到ISpatialIndex对象上去
ISpatialIndex spatialIndex = (ISpatialIndex)geometryBag;
spatialIndex.AllowIndexing = true;
spatialIndex.Invalidate();IQueryDef2接口
IQueryDef对象可由IFeatureWorkspace.CreateQueryDef 方法创建
注意事项:
1)只能在ArcSDE、PGDB、FGDB数据源上使用(注意:shp数据不支持),数据集的历史表示 不被QueryDef游标支持(翻译可能不太准确,详见官方文档)。
2)支持多表查询,但是查询的结果不能进行修改!
3)使用IQueryDef查询出来的游标,用此游标获取的字段的别名和字段名一致(如果是要获取字段的中文别名,请使用其他方法获取游标)
属性及方法详解
- Tables
查询的表名称,支持多表查询,用逗号隔开即可,如”TableUser,TableRole”**
注意事项:如果使用的是SDE数据源,当当前的工作空间不是表所在的用户空间下,需要在表的前边加用户名前缀(如:Owner.MyTable) - SubFields
查询的字段列表,默认不填为查询所有字段,即”*”,支持Distinct关键字,
格式:
1) “*” 返回所有字段
2)”field1,field2,field3” 用逗号隔开要查询的字段
3)”table1.*,table2.field1,table3.field2” 查询table1的所有字段,table2的字段1,和table3的字段2 - WhereClause
这块注意不同数据源,查询的SQL写法不同 - PrefixClause
前缀查询条件,在Select 和 Select Column List之间,如Distinct关键字和ALL关键字 - PrefixClause
后缀查询条件,在Select语句后,紧跟Where语句之后,如Order By - Evaluate
返回ICursor对象,这块使用的过程中记得用ComReleaser管理,在使用完毕释放Com对象。
相关接口
IQueryName2
同创建游标一样,IQueryDef对象能用于生成一个虚拟的表或要素类。示例代码如下:
// Create a reference to a TableQueryName object.
IQueryName2 queryName2 = new TableQueryNameClass();
queryName2.PrimaryKey = String.Empty;
// Specify the query definition.
queryName2.QueryDef = queryDef;
// Get a name object for the workspace.
IDataset dataset = (IDataset)workspace;
IWorkspaceName workspaceName = (IWorkspaceName)dataset.FullName;
// Cast the TableQueryName object to the IDatasetName interface and open it.
IDatasetName datasetName = (IDatasetName)queryName2;
datasetName.WorkspaceName = workspaceName;
datasetName.Name = tableName;
IName name = (IName)datasetName;
// Open the name object and get a reference to a table object.
ITable table = (ITable)name.Open();示例代码
// 创建IQueryDef2对象
IQueryDef2 queryDef2 = (IQueryDef2)featureWorkspace.CreateQueryDef();
// 设置查询的表、字段及后缀查询条件
queryDef2.Tables = "Cities";
queryDef2.SubFields = "Name, Pop1996";
queryDef2.PostfixClause = "ORDER BY Pop1996 DESC";
// 执行查询
属性及方法详解(ComReleaser comReleaser = new ComReleaser())
{
ICursor cursor = queryDef2.Evaluate2(true);
comReleaser.ManageLifetime(cursor);
int nameIndex = cursor.FindField("Name");
int pop1996Index = cursor.FindField("Pop1996");
IRow row = null;
while ((row = cursor.NextRow()) != null)
{
String cityName = Convert.ToString(row.get_Value(nameIndex));
int population = Convert.ToInt32(row.get_Value(pop1996Index));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: {1}", cityName, population);
}
}
执行空间查询
参考官方教材:传送门
数据表排序
使用ITableSort接口对有ObjectIDs的表(或要素类)进行排序。使用该接口进行排序,必须设置Fields属性和Table(或SelectionSet)属性。
ITableSort接口
- 参数
| 可写 | Ascending | |
|---|---|---|
| 可写 | CaseSensitive | CaseSensitive Character fields case sensitive. Default: False. |
| 可写 | Compare | Compare call back interface. Specify Null (default) for normal behavior. |
| 可写 | Cursor | The cursor of the data to sort on. Ensure that sorting fields are available. Cancels SelectionSet. |
| 可写 | Fields | Comma list of field names to sort on. |
| 可读 | IDByIndex | A id by its index value. |
| 可读 | IDs | IDs List of sorted IDs. |
| 可读可写 | QueryFilter | The query filter on table or selection set. |
| 可读 | Rows | Cursor of sorted rows. |
| 可读可写 | SelectionSet | The selection set as a source of the data to sort on. Cancels Cursor. |
| 方法 | Sort | Sort rows. |
| 可写 | SortCharacters | Number of characters to sort on, for string fields. A null (default) sorts on the whole string. |
| 可读可写 | Table | The table as a source of the data to sort on. |
– 示例代码
1.排序必须设置的属性
// 打开要素类"counties"
IFeatureClass featureClass = featureWorkspace.OpenFeatureClass("Counties");
ITable table = (ITable)featureClass;
// 创建一个ITableSort接口对象
ITableSort tableSort = new TableSortClass();
tableSort.Table = table;
// 如果标识连接数据后的结果,记得完整的引用字段
tableSort.Fields = "State_Name, Name"; // "Name"字段是Country name字段
排序的几种组合方式
- Table 对表进行排序
- Table + Cusror 使用游标对表进行排序
- Table + QueryFilter 对使用过滤器的表进行排序
- SelectionSet 对选择集进行排序
- SelectionSet + QueryFilter 是使用过滤器的选择集进行排序
示例代码
IQueryFilter queryFilter = new QueryFilterClass();
queryFilter.WhereClause = "POP > 10000";
tableSort.QueryFilter = queryFilter;设置排序的其它参数
- Ascending 升序
- CaseSensitive 只对文本字段有效,大小写敏感(默认为False,大小写不敏感)
- SortCharacters 只对文本字段有效,按指定的字符进行排序(默认为空)
示例代码
tableSort.set_Ascending("State_Name", false);
tableSort.set_Ascending("Name", true);
tableSort.set_CaseSensitive("State_Name", true);
tableSort.set_CaseSensitive("Name", true);
执行排序
tableSort.Sort(null);// ITrackCancel,支持取消操作
访问排序的结果
- 使用Rows属性读取排序后的结果
// 获取排序后的游标对象
ICursor cursor = tableSort.Rows;
// 获取字段所以
int stateNameIndex = cursor.Fields.FindField("State_Name");
int countyNameIndex = cursor.Fields.FindField("Name");
int popIndex = cursor.Fields.FindField("POP");
// 遍历行 并取得相关的字段值
while ((row = cursor.NextRow()) != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}, {2}", row.get_Value(stateNameIndex), row.get_Value
(countyNameIndex), row.get_Value(popIndex));
}- 使用IDs属性读取排序后的结果
// Get an enumerator of ObjectIDs for the sorted rows.
IEnumIDs enumIDs = tableSort.IDs;
// Get field indexes for efficient reuse.
int stateNameIndex = table.FindField("State_Name");
int countyNameIndex = table.FindField("Name");
int popIndex = table.FindField("POP");
int id = - 1;
IRow row = null;
while ((id = enumIDs.Next()) != - 1)
// -1 is returned after the last valid ID is reached.
{
row = table.GetRow(id);
Console.WriteLine("{0} , {1} , {2}", row.get_Value(stateNameIndex),
row.get_Value(countyNameIndex), row.get_Value(popIndex));
}
自定义排序
自定义类实现ITableSortCallBack接口,实现自己的Compare方法即可进行自定义排序。
ITableSort tableSort = new TableSortClass();
tableSort.Compare = new StreetNumberSort();
tableSort.Table = table;
tableSort.Fields = "StreetNum";
public class StreetNumberSort: ITableSortCallBack
{
public int Compare(object value1, object value2, int fieldIndex, int fieldSortIndex)
{
// Seperate the numeric and non-numeric components of each value.
int value1Number = - 1;
int value2Number = - 1;
String value1Suffix = null;
String value2Suffix = null;
SeperateValues(value1.ToString(), out value1Number, out value1Suffix);
SeperateValues(value2.ToString(), out value2Number, out value2Suffix);
// Compare the numeric components of the street numbers.
if (value1Number != value2Number)
{
// If value1 is less than value2, return -1; otherwise, return 1.
if (value1Number < value2Number)
{
return - 1;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
}
// The numeric values are equal. Compare the suffixes.
int compareResult = String.Compare(value1Suffix, value2Suffix);
if (compareResult < 0)
{
return - 1;
}
else if (compareResult == 0)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
}
private void SeperateValues(String streetNumber, out int number, out Strin suffix)
{
// Step through the street number to the end or until a null character is reached.
StringBuilder numberBuilder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder suffixBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < streetNumber.Length && streetNumber[i] != '\0'; i++)
{ Char currentChar = streetNumber[i];
if (currentChar >= '0' && currentChar <= '9')
{
numberBuilder.Append(currentChar);
}
else
{
suffixBuilder.Append(currentChar);
}
}
// Set the outbound parameters.
Int32.TryParse(numberBuilder.ToString(), out number);
suffix = suffixBuilder.ToString();
}
}连接数据
两种连接数据,关联查询的方法:
– 使用IQueryDef接口进行关联查询
– 使用RelQueryTables 进行关联查询
示例代码:
这里写代码片数据操作
对数据进行插入、更新、删除时最好是开始事务编辑,这样当遇到异常时不会损坏数据,而且也可以进行回滚操作。
数据编辑模式
IWorkspaceEdit接口
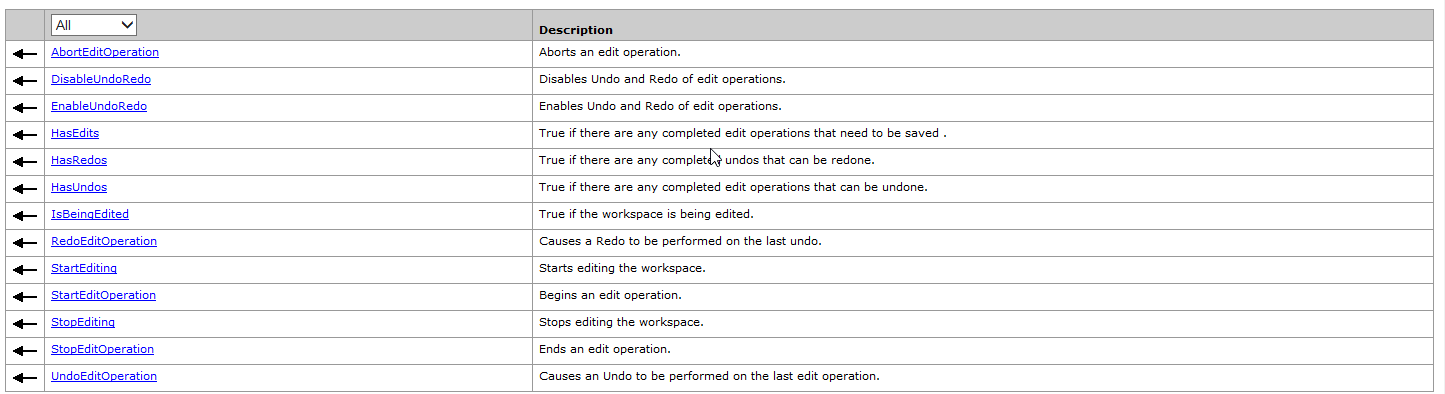
StartEditing (boolwithUndoRedo):开启编辑流程(恢复/取消恢复)
StartEditOperation:开始编辑操作
StopEditOperation:结束编辑操作,用来确保编辑操作的完成
StopEditing (boolsaveEdits):结束编辑流程(保存编辑结束编辑流程或不保存编辑结束编辑流程)
UndoEditOperation:用于编辑状态的回滚操作。
RedoEditOperation:用于编辑状态的恢复操作。
AbortEditOperation:取消所有的编辑操作。
数据插入
数据插入有两种方式,一种通过游标进行插入,一种通过创建新行来插入。
示例代码
- 表插入记录
using(ComReleaser comReleaser = new ComReleaser())
{
ICursor pCursor=pTable.Insert(true);
comReleaser.ManageLifetime(pCursor);
IRowBuffer pRowBuffer=pTable.CreateRowBuffer();
comReleaser.ManageLifetime(pRowBuffer);
//设置属性(此处代码略)
int iFieldIndex=pTable.FindField("FieldName");
pRowBuffer.set_Value(iFieldIndex,"FieldValue");
pCursor.InsertRow(pRowBuffer);
pCursor.Flush();
}- 要素类插入记录
IRow pRow=pTable.CreateRow();
pRow.set_Value(iFldIndex,fieldValue);
pRow.Store();使用技巧
大量插入数据的时候,用游标插入更快,可以每几千条Flush一次,而不是每插入一条就Flush一次。
数据更新
数据更新有两种方式,一种通过游标进行更新,一种是直接更新。
示例代码
游标更新
ICursor pCursor = pTable.Update(pQueryFilter, false);//建议使用False进行更新
pRow.set_Value(iFldIndex1,fieldValue1);
pRow.set_Value(iFldIndex2,fieldValue2);
pCursor.UpdateRow(pRow);直接更新
pRow.set_Value(iFldIndex1,fieldValue1);
pRow.set_Value(iFldIndex2,fieldValue2);
pRow.Store();使用技巧
在更新数据的时候,建议开始编辑模式,以防数据编辑失败,还有就是大量数据更新,建议用游标进行更新,效率会更高。
数据删除
数据删除有好几种方式,1)通过执行SQL进行删除 2)通过更新游标删除 3)直接查询删除 4)直接删除查询的行
示例代码
略
请参考:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5e4c933d010116n5.html
使用技巧
删除的时候一定要注意开启编辑模式
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/yh0503/article/details/53493583



