Scrambled Polygon (极角排序)
|
Language:
Scrambled Polygon
Description
A closed polygon is a figure bounded by a finite number of line segments. The intersections of the bounding line segments are called the vertices of the polygon. When one starts at any vertex of a closed polygon and traverses each bounding line segment exactly
once, one comes back to the starting vertex. A closed polygon is called convex if the line segment joining any two points of the polygon lies in the polygon. Figure 1 shows a closed polygon which is convex and one which is not convex. (Informally, a closed polygon is convex if its border doesn’t have 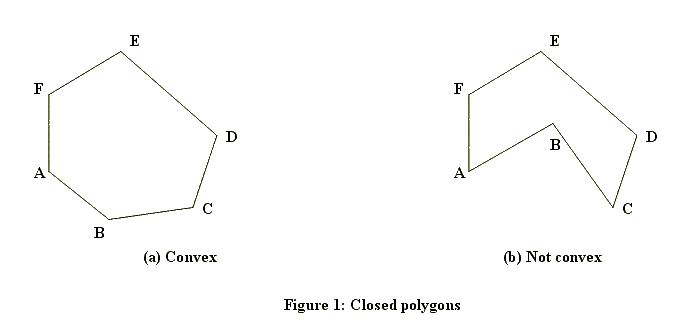 The subject of this problem is a closed convex polygon in the coordinate plane, one of whose vertices is the origin (x = 0, y = 0). Figure 2 shows an example. Such a polygon will have two properties significant for this problem. The first property is that the vertices of the polygon will be confined to three or fewer of the four quadrants of the coordinate plane. In the example shown in Figure 2, none of the vertices are in the second quadrant (where x < 0, y > 0). To describe the second property, suppose you “take a trip” around the polygon: start at (0, 0), visit all other vertices exactly once, and arrive at (0, 0). As you visit each vertex (other than (0, 0)), draw the diagonal that connects the current vertex with   Input
The input lists the vertices of a closed convex polygon in the plane. The number of lines in the input will be at least three but no more than 50. Each line contains the x and y coordinates of one vertex. Each x and y coordinate is an integer in the range -999..999.
The vertex on the first line of the input file will be the origin, i.e., x = 0 and y = 0. Otherwise, the vertices may be in a scrambled order. Except for the origin, no vertex will be on the x-axis or the y-axis. No three vertices are colinear. Output
The output lists the vertices of the given polygon, one vertex per line. Each vertex from the input appears exactly once in the output. The origin (0,0) is the vertex on the first line of the output. The order of vertices in the output will determine a trip
taken along the polygon’s border, in the counterclockwise direction. The output format for each vertex is (x,y) as shown below. Sample Input 0 0 70 -50 60 30 -30 -50 80 20 50 -60 90 -20 -30 -40 -10 -60 90 10 Sample Output (0,0) (-30,-40) (-30,-50) (-10,-60) (50,-60) (70,-50) (90,-20) (90,10) (80,20) (60,30) |
题意:从第一个点开始逆时针输出组成多边形的点。判断向量p1=(x1,y1)到p2=(x2,y2)是否做左
转,只需要判断x1*y2-x2*y1(这个又是叉积吧!!!) 的正负。将第一个点作为参照进行极角排序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct point
{
int x,y;
}A[55];
int cp(point p1,point p2,point p3)
{
return (p1.x*p3.y-p3.x*p1.y)-(p2.x*p3.y-p3.x*p2.y);
}
bool cmp(point a,point b)
{
return cp(A[0],a,b)<0;
}
int main()
{
int n=0;
while(scanf("%d%d",&A[n].x,&A[n].y)!=EOF)
n++;
sort(A+1,A+n,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("(%d,%d)\n",A[i].x,A[i].y);
}
}
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32426313/article/details/52626375