基于pgrouting的路径规划之一
目录
最近接触pgrouting。把学习的结果记录下来。
利用pgrouting进行路径规划只能导入line数据,mutiline会出错。这一点在进行数据导入的时候需要注意。
一、创建数据库
有两种方法:
1.pgadmin可视化工具创建
直接把数据道路postgis模版数据库或以postgis模版数据库为模版创建数据库,这样创建的数据库直接支持空间查询和空间分析。
2.命令行创建数据库
创建数据库
createdb -U postgres routing
让数据库支持PostGIS和pgRouting的函数和基础表
CREATE EXTENSION postgis;CREATE EXTENSION pgrouting;
CREATE EXTENSION postgis_topology;
CREATE EXTENSION fuzzystrmatch;
CREATE EXTENSION postgis_tiger_geocoder;
CREATE EXTENSION address_standardizer;
二、把shp数据导入空间数据库
两种方式:
1.是用可视化工具
(a)打开postgis工具
postgis安装目录下的PostGISShapefile Import/Export Manager
会弹出对话框
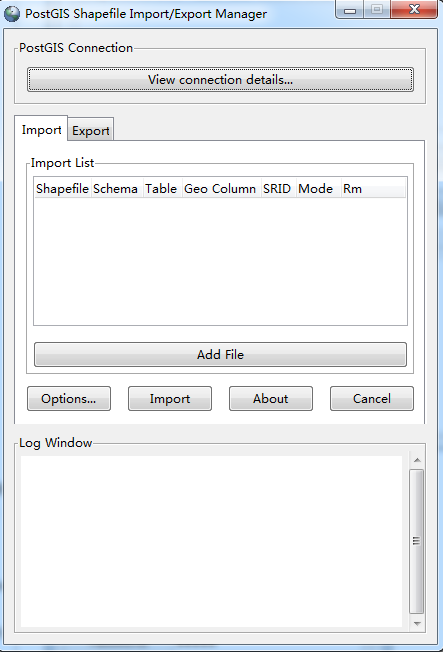
(b)设置数据库连接
单击view connection details,设置数据库的连接
(c)添加shp数据
添加需要导入的shp文件
单击Add File ,会弹出文件选中对话框
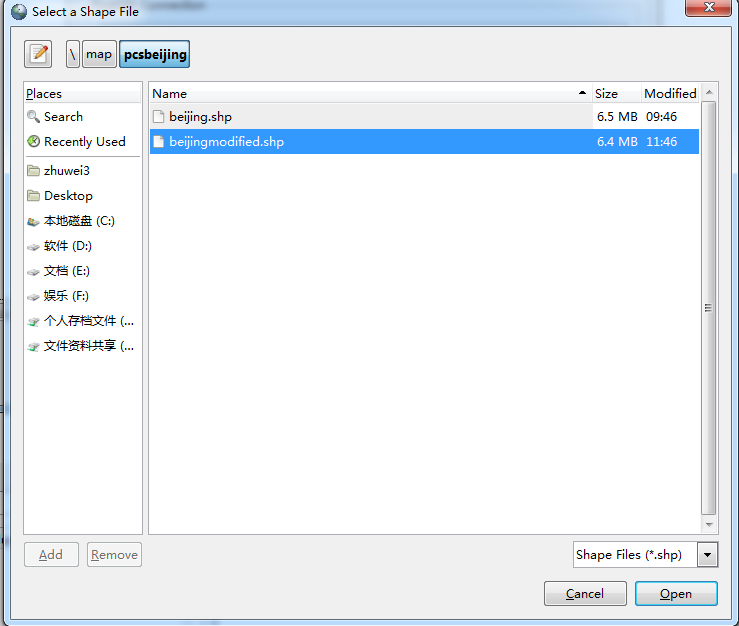
选择需要导入是shp文件,注意此处路径一定要是英文,否则会导入失败
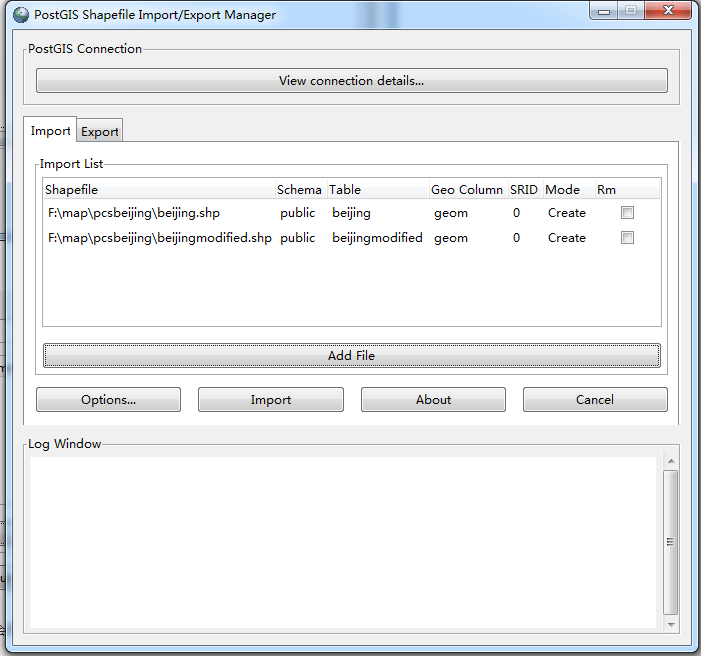
(d)编码设置
单击options,设备编码格式为GBK,选中generate simple geometries instead of multi geometries。
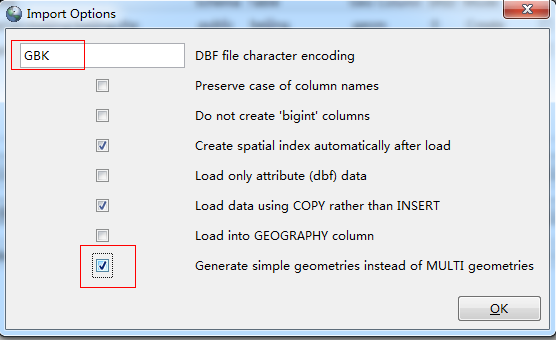
此处导入的shp数据一定要是单线的,否则无法完成路径计算。
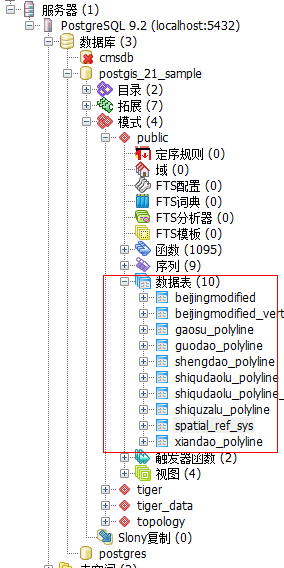
(e)查看导入数据
成功导入数据之后就能在postgresql中看到导入的数据表
2.命令行导入数据
先用shp2psql.exe程序把shp文件装换成sql脚本,
格式为:shp2pgsql 路径\shp数据文件名 新建的数据表名 > 路径\SQL文件名.sql
shp2pgsql -s 4326 beijingmodified public.beijingmodified > beijingmodified.sql
执行得到的sql文件
psql -U postgres -d routing -f beijingmodified.sql
三、创建路网拓扑结构
//添加起点id
ALTER TABLE public.beijing ADD COLUMN source integer;
//添加终点id
ALTER TABLE public.beijing ADD COLUMN target integer;
//添加道路权重值
ALTER TABLE public.beijing ADD COLUMN length double precision;
//为sampledata表创建拓扑布局,即为source和target字段赋值
SELECT pgr_createTopology(‘public.beijing’,0.00001, ‘geom’, ‘gid’);
//为source和target字段创建索引
CREATE INDEX source_idx ON beijingmodified(“source”);
CREATE INDEX target_idx ON beijingmodified(“target”);
//为length赋值
update beijingmodified set length =st_length(geom);
//或者用已有的字段长度赋值,下面shape_length为shp中已有的长度属性
UPDATE beijingmodified SET length = shape_length;
//为beijingmodified表添加reverse_cost字段并用length的值赋值
ALTER TABLE beijingmodified ADD COLUMN reverse_cost double precision;
UPDATE beijingmodified SET reverse_cost =length;
四、尝试查询
使用pgr_dijkstra算法查询
SELECT seq, id1 AS node, id2 AS edge, costFROM pgr_dijkstra(‘
SELECT gid AS id,
source::integer,
target::integer,
length::double precision AS cost
FROM beijingmodified’,
30, 60, false, false);
//查询每个路段经过的点
SELECT st_astext(geom) FROM pgr_dijkstra(‘
SELECT gid AS id,
source::integer,
target::integer,
length::double precision AS cost
FROM beijingmodified’,
30, 60, false, false) as di
join beijingmodified pt
on di.id2 = pt.gid;
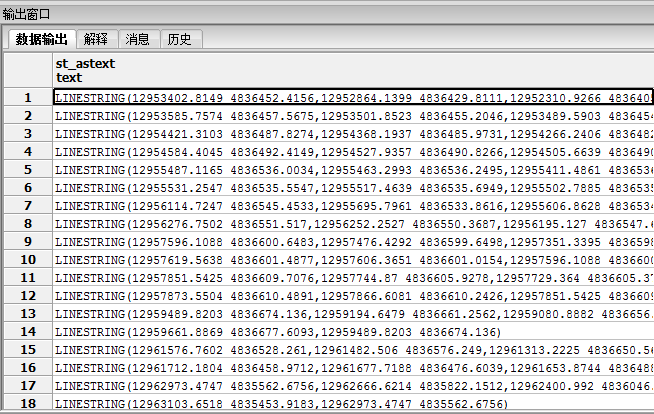
//把查询结果放在新建的表格中
SELECT seq, id1 AS node, id2 AS edge, cost,geom into dijkstra_res FROM pgr_dijkstra(‘
SELECT gid AS id,
source::integer,
target::integer,
length::double precision AS cost
FROM beijingmodified’,
30, 60, false, false) as di
join beijingmodified pt
on di.id2 = pt.gid;
/*
pgr_dijkstra的定义是pgr_costResult[]
pgr_dijkstra(textsql, integer source, integer target, boolean directed, boolean has_rcost);
directed是否限制方向,has_ rcost作用未知,返回值为pgr_costResult。
pgr_costResult在workshop中的解释是
A set of records to describe a path resultwith cost attribute
一组带有消耗属性的用于描述路径结果的记录的集合。
其定义如下
CREATE TYPE pgr_costResult AS
(
seq integer, — rowsequence
id1 integer, — node ID
id2 integer, — edge ID(-1 for the last row)
cost float8 — cost totraverse from id1 using id2
);
*/
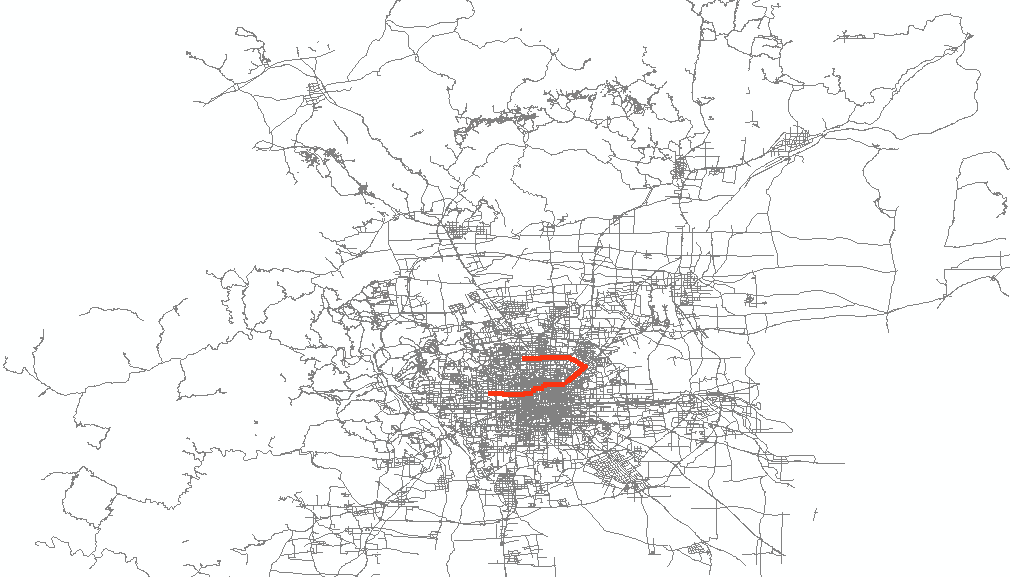
将这个表导出为shp,再在arcmap中定义坐标系打开,可以看到上面的结果如下图所示
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/longshengguoji/article/details/45565551


